No products
To be determined
Shipping
0,00€
Total
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
Quantity
Total
There are 0 items in your cart.
There is 1 item in your cart.
Total products
Total shipping
To be determined
Total
Principles of cut for dental implants installation
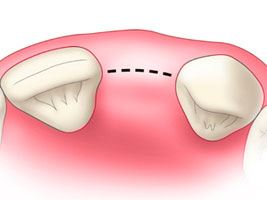
There is a necessity to plan a location, shape and length of the cut with the creation of optimum access and smallest tissues damage. This will ensure a good wound healing, reduce a risk of damage to the nerve fibers and will make a good opportunity to review defects, depressions and holes in the bone. Lowering the flap is usually held periotomom or trimmer Mitchell, allowing preventing a rupture of the flap.
Requirements for the cut:
• Ensure a good access and review the surgical field;
• Must not interfere with the imposition of surgical template;
• Provide the ability to identify important anatomical structures, such as mental hole, incisive canal, as well as the contours of adjacent teeth and zone or retractions crown surface of the bone;
• Must have a clean edge, providing a good wound closure and healing by first intention;
• Allow to form well vascularized mucoperiosteal flap;
• Minimize the amount of scarring and thus prevent decrease the depth of the vestibule.
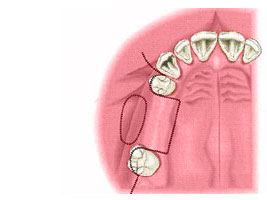
Maxilla. Incision along the crest
It could be cut with a laxative and without it. Requirements for laxative cut of the section:
• Should provide the surgeon needed review. This is particularly important in the presence of cavities on the buccal surface ridge;
• Ensure a good access to overlay template;
• Reduce the likelihood of rumen;
• Minimize the possibility of reducing the vestibule depth in the formation rumen.
This incision was previously standard in conducting a two-stage implantation because it provided protection and complete implant closure at the time of integration. Besides it contributed a good vascularization. Initially there were thoughts that the cut should take place away from the zone of implantation. The advantage of such approach was the absence of contamination of implant cavity with mouth microorganisms and distance cut line from the implant. However, it well known that there is no a significant difference in the outcome implantation during the cut comb through and through the threshold.
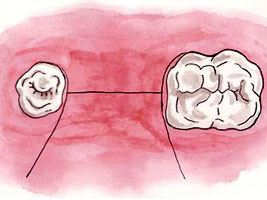 Earlier horizontal suturing was chosen when fixing flap, but the disadvantage of this technique was reducing the depth of the vestibule and education scarring (Figure 5.8). Small eve will impede the imposition of the prosthesis after implantation if there weren't grinding a significant amount of plastic from the vestibular artificial hand alveolar part of the prosthesis. Their insufficient reduction leads to dehiscence wounds.
Earlier horizontal suturing was chosen when fixing flap, but the disadvantage of this technique was reducing the depth of the vestibule and education scarring (Figure 5.8). Small eve will impede the imposition of the prosthesis after implantation if there weren't grinding a significant amount of plastic from the vestibular artificial hand alveolar part of the prosthesis. Their insufficient reduction leads to dehiscence wounds.

Mandible. Incision along the crest
This method provides the same advantages as using in the upper jaw. For cutting tissues while detection of mental holes and knee chin nerve is better to use a blunt instrument. Branch tissue blunt instrument shows the direction which the lower alveolar nerve comes to mental opening: distally or mezial and helps to confirm what has already were detected on radiographs. Pivoted muco-periosteal flap in the field of mental holes is better to refrain from using metal tools; tilting could be performed by using wet gauze.


